
Growing cannabis successfully isn’t just about good genetics or strong nutrients—it’s about timing. A cannabis growing calendar gives growers a clear roadmap of what to do each month, from germinating seeds in early spring to harvesting buds in the fall. Whether you’re cultivating outdoor cannabis in seasonal climates or managing a year-round indoor grow room, following a structured calendar ensures healthier plants, fewer mistakes, and better harvests.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through a month-by-month cannabis growing schedule, explain the differences between indoor and outdoor growing timelines, and share regional variations so you can adapt the calendar to your location. By the end, you’ll know exactly when to plant, train, flower, and harvest cannabis for maximum yields.
A cannabis growing calendar is a month-by-month schedule that guides growers through planting, vegetative growth, flowering, and harvest based on climate or indoor cycles. It helps maximize yields by aligning each stage of the cannabis life cycle with the right season or light schedule.
Why a Cannabis Growing Calendar Matters
In this section, we will read about aligning plant cycles, preventing stress, planning control.
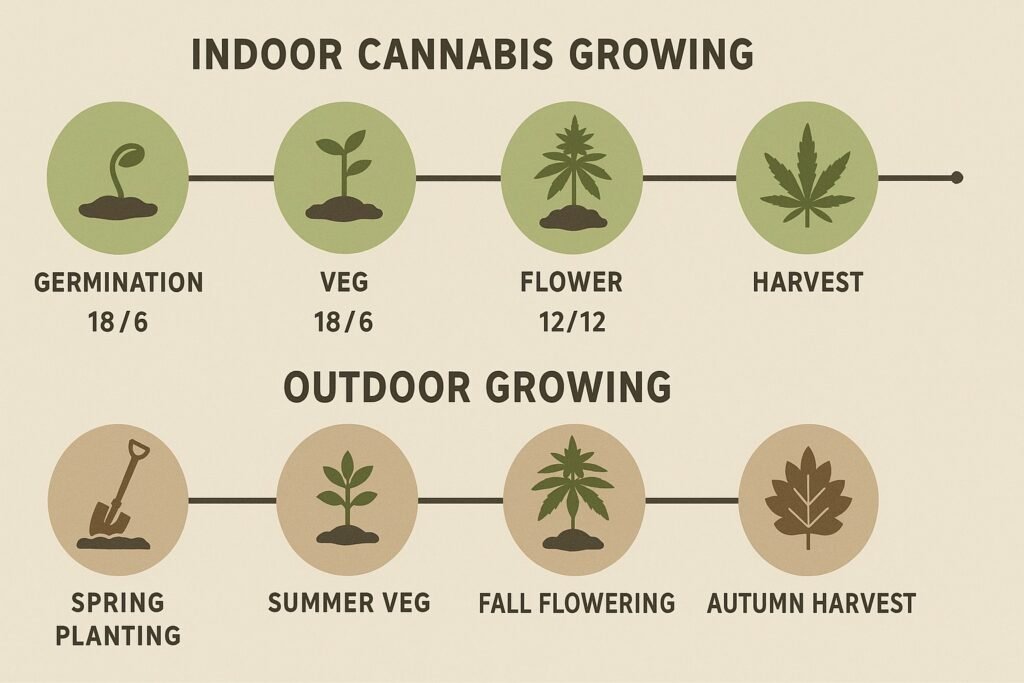
Aligning Plant Cycles With Climate and Light
Cannabis is a photoperiod-sensitive plant, which means its growth depends on the amount of light it receives. Outdoors, the natural seasonal daylight cycle controls when cannabis switches from vegetative growth to flowering. A growing calendar helps you align seed germination, vegetative training, and flowering with the seasonal climate in your region, so plants don’t get stressed or stunted. Indoors, a calendar ensures you maintain the right light schedule (18/6 for veg, 12/12 for flower) without guesswork, keeping your grow consistent.
Preventing Stress and Maximizing Yields
When cannabis plants are exposed to irregular cycles—such as early frost, heat waves, or light leaks indoors—they may turn hermaphroditic, stop producing buds, or suffer nutrient deficiencies. A structured growing calendar reduces these risks by guiding you on when to transplant seedlings, apply nutrients, or begin flowering. Following a predictable cycle keeps your plants healthy and boosts bud density, resin production, and final yield, which is especially important for both home growers and commercial cultivators.
Planning Indoor vs. Outdoor Grows Efficiently
Indoor growers often enjoy more flexibility since artificial lights mimic the sun, but without a calendar, it’s easy to mismanage stages. A cannabis growing calendar for indoor grows helps you track weeks in each phase, preventing plants from being kept in veg too long or flipped to flower too early. For outdoor growers, the calendar provides a regional planting and harvest guide, ensuring you don’t start seeds too soon or miss the ideal harvest window before frost arrives. This balance between indoor control and outdoor seasonality makes the calendar an essential tool for every grower.
Cannabis Growth Stages and Timing Basics
Growing cannabis successfully means understanding its life cycle. Each stage requires a different balance of light, nutrients, and time. Whether you’re following an indoor grow calendar or relying on seasonal outdoor cycles, knowing the approximate timeline helps you avoid mistakes and keep plants thriving.
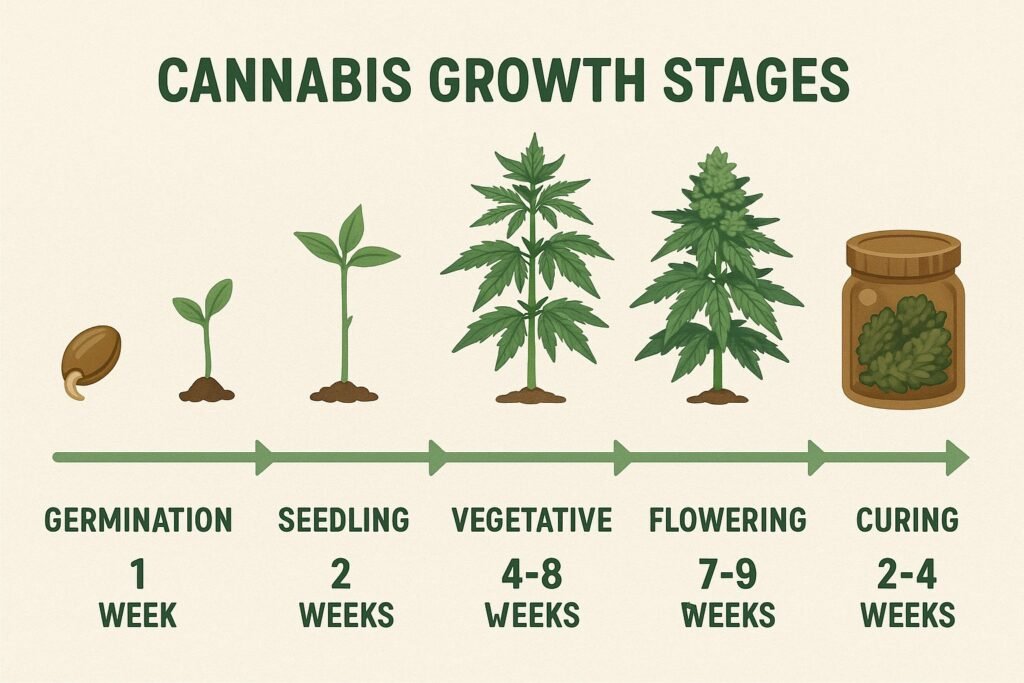
Germination (1–2 weeks)
The cannabis life cycle begins with germination. Seeds need warmth, moisture, and darkness to sprout. In this stage, taproots emerge and the first cotyledon leaves appear. Outdoors, growers typically germinate seeds indoors in early spring to protect them from frost. Indoors, germination can be done year-round using starter cubes, paper towel methods, or small pots.
Seedling Stage (2–3 weeks)
Once the seed has sprouted, the plant enters the seedling stage, producing its first sets of true leaves with serrated edges. During this delicate phase, seedlings require 18–24 hours of light, high humidity (65–70%), and light watering to avoid root rot. Many growers keep seedlings indoors—even for outdoor grows—until they are strong enough to handle natural weather conditions.
Vegetative Stage (4–8 weeks or more)
The vegetative stage is all about building a strong structure. Plants focus on leaf, branch, and root development, preparing for heavy buds later. In outdoor grows, this phase typically runs from late spring to midsummer. Indoors, growers maintain 18 hours of light and 6 hours of darkness (18/6) to encourage rapid growth. Nutrient requirements increase, especially nitrogen, and growers often train plants using topping, LST (low-stress training), or SCROG methods to maximize canopy space.
Flowering Stage (6–10 weeks)
When daylight hours shorten outdoors (late summer to fall), cannabis naturally enters the flowering stage. Indoors, this is triggered by switching the light cycle to 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness (12/12). Plants redirect energy toward bud production, requiring higher phosphorus and potassium. This stage is critical for bud size, resin production, and potency, so keeping the light schedule consistent is essential to prevent hermaphroditism or stress.
Harvest Stage
Harvesting typically occurs when trichomes change from clear to milky or amber, signaling peak potency. Outdoors, this aligns with autumn (September–October in the Northern Hemisphere). Indoors, harvest timing depends on strain genetics and flowering duration. Proper harvest timing maximizes cannabinoid and terpene profiles, ensuring the best flavor and effects.
Curing Stage (2–4 weeks or more)
After harvest, buds must be dried and cured to preserve potency and aroma. Curing involves storing trimmed buds in airtight jars, “burping” them daily to release moisture. This process smooths out the smoke, enhances flavor, and extends shelf life. Skipping curing can lead to harsh, unpleasant buds even if the grow was otherwise perfect.
Outdoor Cannabis Growing Calendar (Month-by-Month)
Outdoor cannabis cultivation follows the natural rhythm of the seasons. A cannabis outdoor grow calendar helps you plan from germination in spring to harvest in the fall. While exact timing varies by region, this month-by-month guide gives growers a reliable schedule to maximize yield and reduce mistakes.

Early Spring (March – April): Germination & Preparation
- Start seeds indoors: Most growers germinate seeds indoors in controlled conditions to protect seedlings from late frosts.
- Soil preparation: Begin enriching outdoor beds with compost, organic matter, and nutrients. Healthy soil is the foundation of a successful grow.
- Hardening off seedlings: Gradually expose seedlings to outdoor light and temperature so they adapt before transplanting.
Late Spring (May – June): Transplant & Early Vegetative Stage
- Transplant seedlings outdoors once nighttime temperatures stay consistently above 12–15°C (54–59°F).
- Early vegetative growth: Plants begin focusing on leaf and root development. Provide balanced nutrients with extra nitrogen.
- Pest & weather protection: Set up netting, row covers, or companion plants to deter pests and protect from strong winds or heavy rain.
Summer (July – August): Strong Vegetative Growth
- Rapid growth: Cannabis plants grow tall and wide, sometimes gaining several inches per day. Training techniques like topping, LST, and SCROG can increase canopy size.
- Watering & feeding: In hot climates, ensure consistent watering and boost nutrients to support heavy vegetative demand.
- Pest & disease monitoring: High summer heat encourages pests like spider mites and mold; regular inspection is key.
Fall (September – October): Flowering & Harvest Preparation
- Flowering begins: As daylight hours shorten, plants naturally transition into flowering. Switch feeding to phosphorus and potassium-rich nutrients.
- Trichome monitoring: Watch for milky or amber trichomes as harvest indicators.
- Harvest readiness: Most outdoor cannabis strains are harvested between late September and October, depending on strain and region.
Late Fall (November): Harvest, Drying & Soil Prep
- Harvest completion: Any remaining plants should be cut before the first frost.
- Drying and curing: Hang branches in a cool, dark space with airflow for 7–14 days, then move to jars for curing.
- Preparing for next season: Amend soil with organic matter and cover crops to restore nutrients for the following spring.
Indoor Cannabis Growing Calendar (Year-Round Guide)
Unlike outdoor cultivation, indoor cannabis growing calendars are not tied to the seasons. By using grow lights, controlled temperatures, and humidity systems, you can grow cannabis any time of the year. The key is following a consistent week-by-week schedule for germination, seedling growth, vegetative development, flowering, and harvest.
Germination & Seedling Stage (1–3 Weeks)
- Light cycle: 18–24 hours of low-intensity light per day.
- Humidity & temperature: Keep humidity around 65–70% and temperature between 22–26°C (72–79°F).
- Focus: Roots establish while seedlings develop their first serrated leaves. Indoor growers often use seedling heat mats and humidity domes for faster, healthier starts.
Vegetative Stage (4–8 Weeks or Longer)
- Light cycle: 18 hours on, 6 hours off (18/6) to encourage growth.
- Nutrients: High nitrogen, balanced nutrients for strong root and leaf development.
- Training: Indoor growers can use topping, LST (low-stress training), or SCROG setups to maximize canopy spread under grow lights.
- Goal: Build a strong plant structure that can support heavy buds during flowering.
Flowering Stage (6–10 Weeks)
- Light cycle: Switch to 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness (12/12) to trigger flowering.
- Environment: Reduce humidity to 40–50% and maintain slightly cooler night temperatures to prevent mold and enhance resin production.
- Nutrients: Increase phosphorus and potassium while lowering nitrogen.
- Monitoring: Keep a close eye on trichomes, pistil coloration, and bud density for harvest timing.
Harvest & Curing Stage (2–4+ Weeks)
- Harvesting: Cut plants when trichomes are mostly milky with some amber.
- Drying: Hang branches in a dark, ventilated room at ~18–21°C (65–70°F) and 50% humidity for 7–14 days.
- Curing: Place dried buds in glass jars, burping daily for the first 1–2 weeks, then weekly. Proper curing enhances flavor, aroma, and potency.
Regional Cannabis Growing Calendar Variations
A cannabis growing calendar is not one-size-fits-all. The ideal planting and harvest times depend on your geographic location, climate zone, and local daylight hours. While the general cannabis life cycle remains the same, adapting your schedule to regional conditions ensures stronger plants and bigger yields.
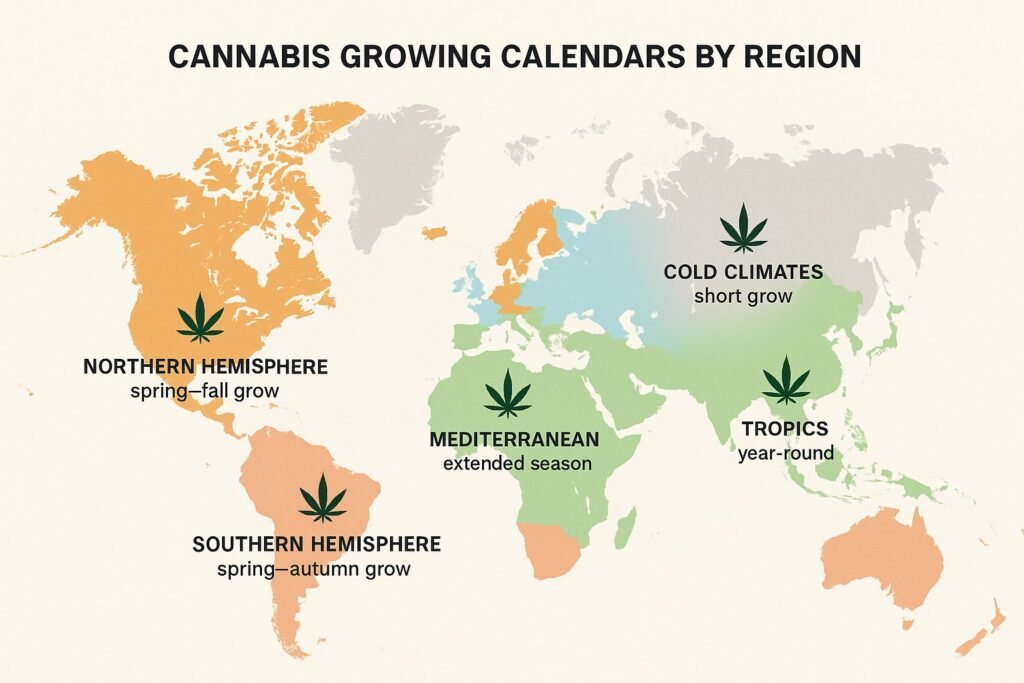
Northern Hemisphere (U.S., Canada, Europe)
- Planting: Germination usually begins indoors in March–April, with outdoor transplants happening in May once frost risk passes.
- Flowering: Plants naturally enter flowering in late July–August as daylight shortens.
- Harvest: Most outdoor harvests occur between late September and October.
- This calendar works well for temperate climates like the United States, Spain, Italy, and most of Europe.
Southern Hemisphere (Australia, South America, South Africa)
- Planting: Seasons are reversed; seeds are germinated in September–October (spring).
- Flowering: Outdoor plants flower in January–February.
- Harvest: Main harvest window is March–April, just before the onset of winter.
- Countries like Australia, Argentina, Chile, and South Africa follow this pattern.
Cold Climates (Northern Europe, Canada, Mountain Regions)
- Challenge: Short growing season with risk of frost in spring and fall.
- Adaptation: Growers often use fast-flowering strains, autoflowers, or greenhouses to beat the cold.
- Planting window: May–June for outdoor transplants.
- Harvest: Usually forced early in September to avoid frost damage.
Warm & Mediterranean Climates (California, Italy, Spain, Middle East)
- Advantage: Long, sunny summers allow for extended vegetative growth and larger yields.
- Planting: March–April with longer veg cycles possible.
- Harvest: Late October to even November for long-flowering sativas.
- Some growers even get two harvests per year by starting early in the season and replanting after summer.
High-Altitude & Tropical Regions
- High-altitude climates: Stronger UV exposure can increase resin production but cold nights may stress plants. Best to choose hardy hybrids.
- Tropical regions: With year-round warmth and relatively stable daylight, growers often rely on autoflowering strains or manipulate light schedules to force flowering.
- Harvests can occur multiple times per year depending on rainfall patterns.
Cannabis Growing Calendar PDF & Printable Chart
One of the easiest ways to stay on track with your grow is to use a visual cannabis growing chart. While written guides are useful, many growers prefer having a month-by-month printable calendar they can pin in their grow room or garden shed. A well-structured cannabis grow calendar PDF acts like a checklist, reminding you exactly when to start seeds, adjust light cycles, feed nutrients, or prepare for harvest.
For outdoor growers, the printable calendar aligns each task with the spring, summer, and fall seasons, helping you plan around your region’s climate. Indoor growers can use the chart as a week-by-week schedule, noting how many weeks their plants have been in seedling, vegetative, or flowering stages.
Offering a downloadable PDF grow calendar also makes it easier for you to keep records. Many successful growers pair their chart with a grow journal, where they write down strain details, nutrient schedules, and yield results. Over time, this creates a personalized reference that helps improve future harvests.

→ Click here to download Cannabis Growing Calendar in pdf.
Tips for Staying on Track With Your Cannabis Growing Calendar
A cannabis growing calendar only works if you stick to it. Many growers, especially beginners, forget key tasks like switching light cycles or adjusting nutrients at the right time. By using a few smart strategies and tools, you can stay consistent and ensure every stage of your grow goes smoothly.

Use a Grow Journal or Logbook
Keeping a cannabis grow journal is one of the most effective ways to track progress. Write down the date of germination, transplanting, nutrient feedings, and signs of flowering. A journal helps you compare results across grows, refine your methods, and avoid repeating mistakes. Many growers now use digital grow log apps that automatically track light cycles, humidity, and feeding schedules.
Set Up Smart Grow Lights and Timers
For indoor growers, timing is critical. Using automated grow light timers ensures your plants always get the correct light cycle—whether it’s 18/6 during vegetative growth or 12/12 during flowering. Many modern LED grow lights connect to smart home systems, allowing you to adjust brightness, spectrum, and timing from your phone. This eliminates human error and keeps your cannabis growth stages on schedule.
Monitor Weather for Outdoor Grows
Outdoor growers must adapt to changing seasonal weather conditions. Keeping an eye on local forecasts helps you prepare for unexpected frosts, heatwaves, or heavy rain. You can use simple weather apps or even install a backyard weather station to track real-time conditions. Aligning your calendar with the climate protects your plants and keeps your outdoor cannabis grow schedule reliable.
Stay Consistent With Nutrient Schedules
Feeding cannabis plants at the right time is just as important as light and temperature. Use your growing calendar to note when to switch from nitrogen-heavy vegetative nutrients to phosphorus and potassium-rich flowering nutrients. Setting reminders for feedings prevents underfeeding or overfeeding, which can delay plant development.
Common Mistakes in Following a Cannabis Growing Calendar
Even with a detailed cannabis growing calendar, many beginners make timing errors that hurt their yields. Understanding the most common mistakes can help you avoid setbacks and keep your grow on track.

Starting Too Early or Too Late Outdoors
Outdoor growers often misjudge the planting season. Starting seeds too early in cold climates exposes them to frost, while planting too late shortens the vegetative stage, leading to smaller plants and lower yields. The cannabis growing calendar exists to align your grow with regional climate and daylight hours, so always check your local frost dates before planting.
Overfeeding or Underfeeding at the Wrong Stage
Many growers fail to adjust nutrients according to growth stages. Feeding heavy nitrogen during flowering can delay bud development, while not providing enough phosphorus and potassium leads to weak, airy buds. A calendar ensures you switch nutrients at the right time, supporting plant needs in each phase. Keeping a nutrient schedule tied to your grow calendar prevents costly mistakes.
Ignoring Light Schedules Indoors
Indoor growers sometimes forget to adjust their light cycle when transitioning from vegetative growth to flowering. Even small light leaks during the dark period can stress plants, causing hermaphroditism or stunted flowering. Following a week-by-week indoor grow calendar ensures that you flip to 12/12 lighting at the right time and maintain consistency.
Missing the Harvest Window
Harvesting too early results in weak potency, while waiting too long can degrade THC into CBN, reducing the uplifting effects. Many growers don’t monitor trichomes and pistils closely. A growing calendar helps remind you to check buds regularly during flowering so you don’t miss the optimal harvest period.
FAQs
In most Northern Hemisphere regions, the best month to plant cannabis outdoors is late May to early June, once the risk of frost has passed. In the Southern Hemisphere, growers typically plant in September–October during spring. For indoor grows, cannabis can be planted any month of the year as long as the correct light cycle is maintained.
Yes. Indoor cannabis cultivation allows for year-round growing because you control light, temperature, and humidity. By following a week-by-week indoor grow calendar, you can germinate, veg, and flower plants any time of year. Many indoor growers run multiple cycles annually, often harvesting 3–4 times per year depending on strain length.
The full cannabis life cycle typically takes 3 to 5 months from seed to harvest, depending on strain genetics and growing conditions. Autoflowering strains can finish in as little as 10 weeks, while photoperiod strains often take 4–6 weeks veg plus 8–10 weeks flowering. A growing calendar helps you map this timeline precisely.
Yes, but with adjustments. Autoflowers do not rely on daylight changes to flower; instead, they automatically transition after 3–5 weeks. While you don’t need to track light cycles, a calendar is still useful to plan feeding schedules, training techniques, and harvest timing.
Always adapt the calendar to your local frost dates, daylight hours, and seasonal weather. In colder climates, start seeds indoors later in spring to avoid frost. In warm or Mediterranean climates, you can extend the vegetative stage or even grow two outdoor harvests in a year. Regional adjustments are key to maximizing yield.
Conclusion
Following a cannabis growing calendar is one of the smartest ways to keep your grow organized, reduce mistakes, and maximize yields. By aligning each stage of the cannabis life cycle with the right timing—whether it’s germination in spring, vegetative growth in summer, or flowering in fall—outdoor growers can take full advantage of natural climate conditions. For indoor growers, a structured week-by-week grow calendar ensures light cycles, nutrient schedules, and harvest timing stay consistent all year long.
A reliable growing calendar also helps you avoid common pitfalls such as planting too early, missing the harvest window, or overfeeding during the wrong stage. Whether you’re cultivating in a backyard garden or a high-tech grow tent, the key to success is planning ahead and sticking to a schedule.
If you’re ready to dive deeper into seasonal cannabis cultivation, check out our Growing Weed Outdoors: Complete Beginner’s Guide. This guide expands on outdoor planting strategies, soil preparation, and regional tips to help you achieve the biggest possible harvests.
Mastering your cannabis growing calendar isn’t just about timing—it’s about creating a system that brings you healthier plants, higher yields, and a smoother growing experience year after year. 🌱✨






