
Growing medicinal hemp isn’t just about planting seeds — it’s about cultivating wellness from the ground up. As laws evolve and the demand for CBD-rich hemp products skyrockets, more small-scale growers and homesteaders are discovering how rewarding it can be to grow medicinal hemp legally and organically. Whether you’re a curious gardener or planning a small CBD farm, understanding the basics of hemp cultivation for medicinal use is essential to success.
Medicinal hemp, unlike industrial varieties, is specially bred for its high cannabidiol (CBD) and low THC content, making it the foundation for many therapeutic oils, balms, and tinctures. To produce high-quality CBD hemp flowers, growers must master the right combination of genetics, soil health, climate, and post-harvest handling. It’s a craft that blends science and sustainability — where each decision, from choosing the right strain to timing your harvest, impacts both potency and compliance.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through everything from selecting certified hemp seeds and nurturing your plants with organic nutrients to harvesting and curing buds for maximum CBD yield. You’ll also learn about licensing requirements, THC testing regulations, and best practices for sustainable hemp farming that align with local laws.
Whether you’re growing hemp outdoors under the sun or managing a small indoor hemp grow setup, this guide will help you cultivate medicinal-grade hemp plants with confidence and care.
🌿 What Is Medicinal Hemp and Why It’s in High Demand

Medicinal hemp, often called CBD hemp, is a specialized variety of the Cannabis sativa plant cultivated primarily for its high cannabidiol (CBD) content and low tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) levels — typically below 0.3%. Unlike psychoactive marijuana, medicinal hemp doesn’t cause a “high.” Instead, it’s grown for its therapeutic and wellness benefits, powering everything from CBD oils and tinctures to capsules, edibles, and skincare products.
What sets medicinal hemp apart from industrial hemp is its phytochemical composition and cultivation purpose. While industrial hemp focuses on fiber, grain, and biofuel, medicinal hemp is carefully bred to produce cannabinoid-rich flowers ideal for CBD extraction. These resinous buds contain valuable compounds like terpenes, flavonoids, and minor cannabinoids such as CBG and CBN, which together create what researchers call the entourage effect — a synergistic boost to the body’s endocannabinoid system.
In recent years, consumer demand for hemp-derived CBD products has exploded, driven by rising awareness of natural wellness alternatives. People are turning to medicinal hemp oil for relief from stress, inflammation, chronic pain, anxiety, and sleep disorders — all without intoxicating side effects. This surge in popularity has turned CBD hemp cultivation into one of the fastest-growing agricultural sectors, attracting farmers, herbalists, and entrepreneurs alike.
Moreover, as more regions legalize hemp farming under agricultural reform acts, opportunities for small growers and organic cultivators have multiplied. The modern hemp industry now thrives on sustainable farming practices, organic certification, and eco-friendly CBD extraction methods, making medicinal hemp not just profitable but also environmentally responsible.
In short, medicinal hemp bridges the gap between natural wellness and modern science — a plant once misunderstood, now recognized for its healing potential, economic promise, and sustainable cultivation value.
🌿 Legal Requirements for Growing Medicinal Hemp
Before planting your first hemp seed, understanding the legal framework for medicinal hemp cultivation is essential. Although hemp is federally legal in many countries, including the United States under the 2018 Farm Bill, growers must comply with strict CBD hemp regulations to ensure their crops remain lawful and marketable.

Medicinal hemp is defined as Cannabis sativa containing less than 0.3% THC (or 0.2% in parts of Europe). This THC threshold separates legal hemp from psychoactive cannabis. To grow hemp for medicinal or CBD purposes, you’ll typically need to apply for a hemp farming license or cultivation permit through your state or regional agricultural department.
Each region has its own set of licensing requirements, which may include:
- Submitting GPS coordinates of your growing site
- Providing a criminal background check
- Registering with your state hemp program or national agricultural board
- Signing agreements to allow random field inspections and THC testing
Once licensed, growers must adhere to testing protocols that verify THC levels before harvest. If the results exceed the legal limit, the crop may need to be destroyed — a costly reminder of how crucial strain selection and harvest timing are for compliance.
In the U.S., the USDA (United States Department of Agriculture) oversees federal hemp regulations, while states such as Colorado, Oregon, and Kentucky have additional local compliance programs. In Europe, EU hemp regulations fall under the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP), which defines approved seed varieties and THC thresholds. Meanwhile, countries like Canada, Australia, and Switzerland operate under their own national hemp licensing systems, each focusing on consumer safety, traceability, and quality assurance.
Growers must also keep detailed hemp cultivation records, including:
- Seed source and certification
- Planting and harvest dates
- Laboratory THC and CBD test results
- Sales and transport documentation
By following these regulations, hemp cultivators not only stay compliant but also build credibility in a rapidly expanding CBD wellness market. Operating legally opens doors to partnerships with CBD manufacturers, wellness brands, and export opportunities across regions where medicinal hemp products are in high demand.
In short, understanding and following the legal requirements for growing hemp is the foundation of a sustainable and trustworthy medicinal hemp operation — ensuring your CBD-rich harvest stays compliant, profitable, and future-proof.
🌿 Choosing the Right Medicinal Hemp Seeds
The success of your medicinal hemp cultivation starts with one crucial decision — choosing the right hemp seeds. Selecting the right genetics determines everything from CBD potency and THC compliance to yield, flavor profile, and disease resistance. In the fast-growing CBD wellness market, using certified high-CBD, low-THC hemp seeds is the foundation of a profitable and legally compliant operation.

When sourcing hemp seeds for medicinal use, always look for certified varieties approved by your country’s agricultural department. Certified seeds are bred to maintain a stable CBD-to-THC ratio, ensuring your crop stays below the legal THC limit (usually 0.3% or less). Using uncertified or untested genetics can result in THC spikes that risk the entire harvest — and your license.
🌱 Feminized vs Regular Hemp Seeds
For CBD production, feminized hemp seeds are the top choice. These seeds are bred to produce almost exclusively female plants, which are the ones that generate cannabinoid-rich flowers used for CBD extraction. Male plants, on the other hand, can pollinate females, leading to seeded buds and lower CBD yields — a costly mistake for growers focused on quality oil production.
Regular hemp seeds (non-feminized) are still used by some traditional farmers or breeders who want to experiment with new hemp crosses and genetics. However, for consistent CBD output, feminized seeds remain the gold standard.
🌿 Top Strains for Medicinal Hemp Cultivation
If you’re aiming for therapeutic-grade CBD hemp, consider reliable and proven high-CBD hemp strains such as:
- Cherry Wine – Known for balanced CBD levels and strong aroma.
- Elektra – A fast-flowering strain with rich terpene profiles.
- Sour Space Candy – Delivers fruity flavor and high resin content.
- Special Sauce – Compact plants with dense CBD buds.
- Wife or Suver Haze – High yield, excellent cannabinoid balance.
Each cultivar offers unique characteristics in flavor, growth behavior, and CBD concentration, so choose based on your region’s climate, soil type, and intended use (e.g., oil extraction vs smokable flower).
🌾 Where to Buy Certified Hemp Seeds
Always purchase from reputable hemp seed suppliers or licensed nurseries that provide full documentation — including seed origin, cannabinoid profile certificates (COAs), and germination rates. Buying cheap, uncertified seeds might seem like a shortcut, but it often results in poor genetic stability, THC compliance issues, or low CBD output.
Also, consider the seed’s germination rate (preferably above 90%) and disease resistance traits. Quality genetics save growers from future losses caused by pests, mold, or environmental stress.
🌿 Ideal Growing Conditions for Medicinal Hemp
To grow potent, compliant, and high-yielding medicinal hemp plants, you need to create the perfect environment where the crop can truly thrive. Unlike industrial hemp, CBD-rich hemp varieties demand more controlled and nutrient-rich conditions. Whether you’re growing indoors or outdoors, the right soil, climate, light, and moisture balance will determine the quality of your CBD content and overall plant health.

🌞 Climate and Temperature
Medicinal hemp performs best in warm, temperate climates with consistent sunlight and moderate humidity levels. Ideally, the growing season should have at least 6–8 hours of direct sunlight daily. The optimal temperature range for hemp lies between 65°F and 85°F (18°C–29°C). Excessive heat can stress plants and reduce CBD potency, while cold or frost can damage trichomes and slow cannabinoid production. In regions with short summers, consider greenhouse cultivation to extend the growing season and protect your plants from climate fluctuations.
🌾 Soil Type and pH
Healthy hemp starts with living soil. The ideal soil for medicinal hemp is loamy, well-drained, and rich in organic matter. Hemp prefers slightly acidic to neutral soil, with a pH range of 6.0–7.5. To boost nutrient availability, amend your soil with compost, worm castings, humus, and biochar — these organic inputs enhance soil structure and microbial life. Avoid heavy clay or waterlogged soils, as poor drainage can suffocate roots and promote fungal growth. Growers who focus on organic or regenerative soil systems often achieve higher CBD concentration because natural microbes and mycorrhizae improve nutrient uptake and stress resistance.
💧 Watering and Irrigation
While hemp is relatively drought-tolerant, consistent and balanced watering is vital during the vegetative and flowering stages. Overwatering leads to root rot, while underwatering limits nutrient absorption and CBD development. For best results, use a drip irrigation system that maintains steady moisture without saturating the soil. Test your water regularly — hemp prefers pH-balanced water (6.0–7.0) with low sodium levels.
💡 Light and Photoperiod
Medicinal hemp is a photoperiod-sensitive plant, meaning the light cycle influences its flowering stage. During the vegetative phase, maintain 18 hours of light and 6 hours of darkness if growing indoors. Once plants reach maturity, shift to 12/12 (12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness) to trigger flowering. For outdoor grows, nature provides this transition automatically as summer turns to fall. Ensure your plants receive full sun exposure and avoid shaded areas that can reduce CBD yield.
🌬️ Humidity and Air Circulation
Maintain 50–60% relative humidity during the vegetative stage and gradually lower it to 40–50% during flowering to prevent mold and bud rot. If growing indoors, invest in oscillating fans or exhaust systems to keep air moving and regulate temperature. Proper airflow strengthens stems, prevents fungal diseases, and supports trichome development — the resin glands responsible for CBD production.
In essence, medicinal hemp thrives when treated like a premium crop — with attention to every environmental detail. By optimizing soil biology, climate balance, and light exposure, you can cultivate CBD-rich hemp plants that express their full genetic potential while staying legally compliant and naturally healthy.
🌿 Step-by-Step Cultivation Process
Growing medicinal hemp is a process that blends timing, care, and precision. Each growth stage — from germination to harvest — plays a vital role in determining your CBD yield, plant health, and THC compliance. Let’s explore how to cultivate hemp step-by-step like a true cannabis craftsman.
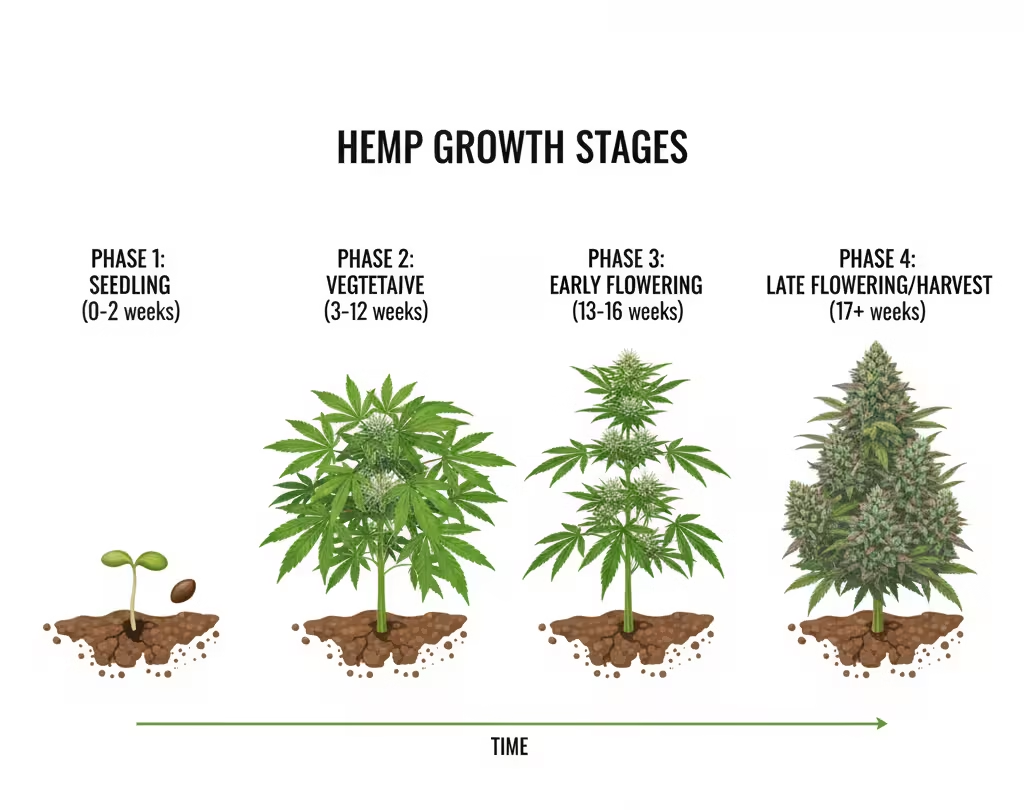
🌱 Germination and Seedling Stage
The journey begins with seed germination, where your hemp seeds awaken into life. Use moist paper towels, seed-starting trays, or peat pellets to germinate seeds in a warm, dark space (70–80°F / 21–27°C). Within 2–5 days, tiny taproots emerge.
Once sprouts appear, gently transfer them into starter pots with organic soil mix rich in perlite and compost. Keep humidity high (around 70–80%) and light moderate to prevent stretching.
Avoid overwatering — hemp seedlings need moisture but hate soggy roots. At this stage, your goal is root development and early vigor. A healthy seedling will have vibrant green leaves and a strong stem ready for transplanting.
🔑 Semantic Tip: Using feminized, high-CBD hemp seeds ensures early stability and reduces the chance of unwanted male plants later.
🌿 Vegetative Stage: Building Strength and Structure
Once transplanted, hemp enters its vegetative stage, where growth accelerates. This is the time to build a strong framework for large CBD flowers later on.
Provide 18 hours of light and 6 hours of darkness if growing indoors. For outdoor growers, plant timing should align with long summer days for maximum sunlight exposure.
Feed your plants with a nitrogen-rich nutrient mix (N-P-K ratio around 3-1-2) to promote lush leaf and stem growth. Organic amendments like worm castings, bat guano, and compost tea work wonders.
Keep the soil evenly moist, maintain a pH of 6.0–7.0, and use gentle air circulation to strengthen stems. Consider low-stress training (LST) or topping to encourage multiple bud sites — a proven trick to boost CBD yield per plant.
💡 Pro Tip: The more light your hemp receives during this phase, the more energy it stores for cannabinoid and terpene production later.
🌸 Flowering Stage: The CBD Gold Rush
As daylight hours shorten (or when you switch your light cycle to 12/12 indoors), your hemp plants begin the flowering phase — the most critical period for CBD resin production.
Buds start forming along nodes, and trichomes (tiny crystal-like glands) develop, giving plants a frosty appearance. Lower nitrogen and increase phosphorus and potassium (N-P-K around 1-3-2) to enhance flower density and cannabinoid synthesis.
Keep humidity between 40–50%, as excess moisture can cause mold or bud rot. During flowering, avoid major pruning — focus on steady watering and light management.
When trichomes turn milky white with some amber, your hemp is at peak CBD potency. This is the perfect time to prepare for harvest.
⚠️ Legal Reminder: Always test your plants for THC content before harvesting to ensure they stay within the 0.3% legal limit.
🧩 Growth Timeline Snapshot
| Growth Stage | Duration | Key Focus | Ideal Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Germination | 2–5 days | Sprouting seeds | Warm, dark, moist |
| Seedling | 2–3 weeks | Root development | 70–80°F, 70% humidity |
| Vegetative | 4–8 weeks | Leaf and stem growth | 18/6 light cycle |
| Flowering | 6–9 weeks | CBD resin formation | 12/12 light cycle, low humidity |
🌾 Final Thoughts on Cultivation
Each phase of hemp growth builds the foundation for the next. Patience, consistency, and observation are your best tools. A grower who understands plant behavior, soil balance, and timing can easily turn a small grow into a high-quality medicinal hemp harvest full of CBD-rich flowers.
🌿 Nutrients and Watering for Maximum CBD Yield
Feeding your hemp plants the right nutrients at the right time is the secret to unlocking their full CBD potential. Medicinal hemp, unlike industrial fiber hemp, demands a balanced nutrient regimen that supports strong vegetative growth and rich resin production during flowering. The goal is to maintain a living, thriving soil ecosystem that feeds your plants naturally — because healthy soil means high CBD yields and superior flower quality.

🌱 Understanding Hemp Nutrition
Like any other crop, hemp relies on three primary macronutrients — nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) — often referred to as the NPK ratio. Each serves a unique purpose:
- Nitrogen (N): Encourages leafy growth and chlorophyll development during the vegetative stage.
- Phosphorus (P): Fuels root growth and flower formation during the flowering stage.
- Potassium (K): Strengthens stems, improves stress resistance, and enhances CBD resin production.
For a balanced nutrient plan:
- Use an NPK ratio of 3-1-2 during the vegetative phase.
- Switch to 1-3-2 or 1-2-3 as plants transition into flowering to focus on bud and cannabinoid development.
🌿 Micronutrients Matter Too
Beyond the basics, hemp plants need small doses of micronutrients such as calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), sulfur (S), iron (Fe), and zinc (Zn). These trace elements play crucial roles in chlorophyll production, enzyme activation, and terpene synthesis — all of which affect aroma, flavor, and CBD concentration.
If your plants show yellowing leaves, curling tips, or weak stems, these are classic nutrient deficiency signs. A simple solution? Feed organically with compost tea, seaweed extract, or Cal-Mag supplements every 1–2 weeks to restore balance.
💡 Pro Tip: Always test your soil or runoff water’s EC (electrical conductivity) and pH — aim for a pH between 6.0 and 7.0 to ensure nutrient absorption stays optimal.
💧 Watering Strategy for Healthy Hemp Growth
Water is life — but too much or too little can quickly ruin your harvest. Medicinal hemp prefers consistent but moderate watering, where roots get moisture without drowning in it.
Follow these watering guidelines:
- Seedling stage: Light misting every 1–2 days to keep the topsoil moist.
- Vegetative stage: Deep watering every 2–3 days once roots are established.
- Flowering stage: Reduce frequency slightly but water deeply to support resin production.
Avoid waterlogging — it cuts oxygen to roots and encourages fungal infections. The best method is drip irrigation or soaker hoses, which deliver steady moisture directly to the root zone while conserving water.
Use filtered or rainwater when possible; chlorine and hard minerals in tap water can harm beneficial soil microbes essential for organic hemp growth.
🌱 Sustainability Tip: Collect rainwater and use mulch around your plants to retain soil moisture naturally. It reduces watering needs and keeps roots cool during hot months.
🧪 Organic Feeding for Maximum CBD Quality
For those pursuing organic or regenerative hemp farming, feed your plants using:
- Compost tea (rich in microbes)
- Molasses water (natural carbohydrate source for soil life)
- Worm castings (slow-release nutrients)
- Fish hydrolysate (high nitrogen and amino acids)
- Bone meal and kelp meal (phosphorus and potassium sources)
These inputs enhance your soil’s living ecosystem, resulting in hemp buds with better terpene expression, stronger flavor profiles, and higher CBD concentration — all without synthetic chemicals.
🌿 Pest and Disease Management in Medicinal Hemp
Even the healthiest hemp garden can face challenges from pests, molds, and diseases that threaten both yield and CBD quality. Because medicinal hemp is cultivated for high-value flowers, every grower must protect plants carefully — not with harsh chemicals, but with organic, eco-friendly pest management strategies that preserve purity and potency.

Unlike industrial hemp, CBD hemp buds are consumed or processed into wellness products, so maintaining chemical-free cultivation is critical for compliance and consumer safety. Let’s look at the best organic pest and disease control techniques that every hemp farmer should know.
🐛 Common Pests That Attack Hemp Plants
Medicinal hemp attracts a variety of small invaders, especially in warm, humid climates. The most common include:
- Aphids: Tiny sap-sucking insects that weaken leaves and stunt growth.
- Spider Mites: Thrive in hot, dry environments and create webbing on leaves.
- Whiteflies: Feed on undersides of leaves, leading to chlorosis and reduced vigor.
- Caterpillars and Cutworms: Chew through stems and buds, damaging flowers.
- Fungus Gnats: Lay eggs in overly wet soil, harming root systems.
💡 Pro Tip: Regularly inspect the undersides of hemp leaves — early detection is the easiest and cheapest form of pest control.
🌼 Organic Pest Control Methods
Instead of synthetic insecticides, use natural pest deterrents and biological controls that keep your plants — and your CBD oil — 100% clean:
- Neem Oil: Acts as a natural insect repellent and antifungal treatment.
- Insecticidal Soap: Made from potassium salts of fatty acids; safe and effective for soft-bodied pests.
- Beneficial Insects: Introduce ladybugs, lacewings, and predatory mites that naturally prey on pests.
- Companion Planting: Grow herbs like basil, dill, marigold, or lavender near hemp — they repel harmful insects and attract pollinators.
- Garlic or Chili Sprays: Simple, DIY foliar sprays that deter common pests naturally.
For outdoor hemp grows, rotating crops each season also reduces pest buildup and promotes healthier soil biodiversity.
🍃 Preventing Mold, Mildew, and Fungal Diseases
Medicinal hemp’s dense buds make it vulnerable to mold and mildew, especially in high humidity. Common culprits include:
- Powdery Mildew: White film on leaves that spreads quickly.
- Botrytis (Bud Rot): Fungal infection that destroys inner buds.
- Root Rot: Caused by overwatering and poor drainage.
To prevent fungal problems:
- Maintain 40–50% humidity during flowering.
- Improve airflow with fans or proper plant spacing.
- Avoid wetting leaves when watering — water the soil base only.
- Apply organic fungicides like potassium bicarbonate or sulfur-based sprays if necessary.
🌿 Sustainability Tip: Mulch your soil and prune lower leaves to increase airflow while conserving moisture — two essential steps to fight mold naturally.
🔄 Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for Hemp
Modern hemp farms often use Integrated Pest Management (IPM) — a holistic approach that combines observation, prevention, and gentle intervention. IPM involves:
- Monitoring plants regularly for early signs of stress or infestation.
- Using biological predators and natural repellents instead of chemicals.
- Adjusting environmental conditions (temperature, humidity, light) to make your grow space less inviting to pests.
- Documenting pest activity to identify patterns seasonally.
This method keeps hemp cultivation sustainable, eco-safe, and compliant with organic hemp certification programs.
🌾 Final Thoughts on Pest and Disease Control
Protecting your hemp plants doesn’t mean fighting nature — it means working with it. By integrating natural pest repellents, biological allies, and smart environmental management, you’ll maintain a clean, pest-free grow while preserving the organic integrity of your CBD-rich harvest.
Healthy plants equal healthy cannabinoids — and a resilient, chemical-free hemp farm always produces premium medicinal flowers ready for wellness use and extraction.
🌿 Harvesting, Drying, and Curing Medicinal Hemp
Harvest time is the most rewarding stage of your medicinal hemp cultivation journey — it’s when months of care finally pay off. But this phase also demands patience and precision. Harvesting too early can reduce CBD potency, while drying or curing improperly can destroy terpenes and flavor. To produce premium-grade hemp flowers suitable for CBD extraction or wellness products, growers must follow a controlled post-harvest process that preserves cannabinoids, aroma, and purity.

🌼 Knowing When to Harvest Hemp
The secret to a successful harvest lies in timing. Medicinal hemp is ready to harvest when CBD concentration peaks and THC levels remain compliant (below 0.3%).
Here’s how to know your plants are ready:
- Trichome Color: Use a magnifying glass or jeweler’s loupe. When trichomes change from clear to milky white with a few amber heads, CBD content is at its highest.
- Pistil Color: Most pistils (the white hairs on buds) will darken to orange or brown and curl inward.
- Aroma & Density: Buds become aromatic, sticky, and dense to the touch.
Avoid waiting too long — prolonged flowering can raise THC levels and risk non-compliance testing issues.
💡 Pro Tip: Always send a lab sample before harvest to verify THC and CBD ratios for legal assurance.
✂️ Harvesting Techniques for Medicinal Hemp
When it’s time to harvest, handle plants gently to protect delicate trichomes — these resin glands hold most of your CBD and terpene content. You can harvest whole plants or individual branches, depending on scale and drying space.
Use sharp sterilized shears and wear gloves to prevent contamination. Hang entire branches upside down to allow air circulation and even drying. Avoid stripping leaves prematurely — they help slow down moisture loss for a smoother cure.
🌬️ Drying Hemp for CBD Preservation
Proper drying is critical to preserving cannabinoids, terpenes, and color.
Dry your hemp in a dark, well-ventilated room with the following conditions:
- Temperature: 60–70°F (15–21°C)
- Humidity: 50–60% RH
- Airflow: Gentle circulation from fans (not directly on buds)
Drying usually takes 7–14 days, depending on bud size and environmental conditions. You’ll know your hemp is ready when stems snap cleanly instead of bending.
Avoid direct sunlight — UV rays can degrade CBD and terpenes quickly. Proper drying ensures flowers retain their natural aroma, cannabinoid profile, and smokable quality.
🌸 Curing: The Final Polish
Once dried, your hemp flowers are ready for curing — a slow, controlled process that enhances flavor, smoothness, and CBD potency stability.
Trim buds from branches and store them in airtight glass jars or food-safe containers. Keep them in a cool, dark place (60–70°F, 55–62% humidity) for 2–4 weeks.
Open the jars daily for the first week (“burping”) to release trapped moisture and prevent mold growth.
Curing allows chlorophyll to break down, resulting in smoother smoke and richer flavor. Most importantly, it helps cannabinoids like CBD and terpenes stabilize — giving your hemp flowers a professional-grade finish perfect for extraction or retail use.
🌿 Pro Tip: Add humidity control packs (58–62%) in curing jars to maintain perfect moisture levels without guesswork.
🪴 Post-Harvest Storage Tips
- Store finished buds in airtight containers away from light and heat.
- Use glass, not plastic, to avoid static and flavor loss.
- Label jars with strain name, harvest date, and test results for traceability.
Properly cured hemp can maintain quality for up to 12 months when stored under ideal conditions.
🌾 Final Thoughts on Harvesting and Curing
The post-harvest process is where average hemp turns into premium medicinal hemp. Taking your time to harvest at peak CBD levels, dry slowly, and cure properly ensures your flowers deliver their true therapeutic potential. A careful grower doesn’t just grow plants — they craft wellness from nature’s most versatile crop.
🌿 Post-Harvest Processing and CBD Extraction
Once your medicinal hemp flowers are perfectly dried and cured, it’s time to transform them into valuable CBD-rich products. This post-harvest phase is where the true potential of your crop is unlocked — through careful trimming, extraction, and refinement that preserve potency, purity, and compliance.

✂️ Trimming and Preparing the Biomass
After curing, trim away sugar leaves and stems to create clean, resinous buds ready for processing. Hand-trimming ensures you preserve delicate trichomes, which contain most of your CBD and terpene content.
The leftover material — including small buds and leaves rich in trichomes — can be collected as biomass for oil extraction. Keep it stored in airtight bags or containers in a cool, dark place until extraction day.
💡 Tip: Don’t over-handle buds; friction and heat can damage trichomes and reduce CBD yield.
🧪 CBD Extraction Methods
CBD can be extracted from hemp flowers using several techniques, each with its own advantages in purity, safety, and scalability.
1. CO₂ Extraction (Most Popular & Cleanest)
This method uses pressurized carbon dioxide to separate cannabinoids and terpenes from plant matter. It’s considered the gold standard because it’s solvent-free, produces clean oil, and allows precise control of temperature and pressure.
- Pros: Chemical-free, consistent purity, ideal for premium products.
- Cons: Requires costly equipment and skilled operation.
2. Ethanol Extraction
Food-grade ethanol dissolves cannabinoids efficiently and works well for large-scale operations. The extract is later purified through winterization (freezing and filtering to remove fats and waxes).
- Pros: Efficient and scalable for commercial CBD oil production.
- Cons: Can strip some terpenes if not carefully managed.
3. Lipid Infusion (Organic Method)
Perfect for small-batch growers. CBD is infused into carrier oils like MCT, olive, or hemp seed oil using gentle heat.
- Pros: Simple, inexpensive, and fully organic.
- Cons: Lower potency and shorter shelf life.
⚗️ Purification and Refinement
After extraction, the crude CBD oil goes through additional refinement steps:
- Winterization: Freezing oil to remove fats and waxes.
- Filtration & Decarboxylation: Heating the extract to activate cannabinoids (turning CBDa into CBD).
- Distillation: Separating cannabinoids for higher concentration and clarity.
These processes yield CBD distillate or isolate, depending on your target product type.
- Full-spectrum: Contains all cannabinoids and terpenes.
- Broad-spectrum: THC removed but retains other beneficial compounds.
- Isolate: 99% pure CBD — ideal for precise formulations.
🧬 Testing and Quality Assurance
Every batch of extracted oil must undergo third-party lab testing to ensure safety and compliance. Labs analyze CBD potency, THC levels, terpene profiles, and contaminants (like heavy metals, pesticides, and solvents).
Proper labeling and Certificate of Analysis (COA) transparency help you build trust and meet legal requirements in regulated CBD markets.
🌿 Sustainability in Hemp Processing
Eco-friendly hemp operations recycle ethanol, reuse CO₂, and minimize waste. Spent biomass can even be repurposed into hemp compost, mulch, or biofuel, completing a zero-waste cultivation cycle that’s both profitable and sustainable.
🌾 Final Thoughts on CBD Extraction
Post-harvest processing is where agriculture meets science. By mastering clean extraction and purification, you can turn your harvested hemp into high-value CBD oils, tinctures, and concentrates that meet both consumer demand and regulatory standards. Precision, purity, and passion — that’s the formula for a truly successful medicinal hemp operation.
🌿 Common Mistakes to Avoid When Growing Medicinal Hemp
Even the most dedicated hemp growers can make errors that impact their CBD yield, THC compliance, and overall crop health. Medicinal hemp is a sensitive plant — it rewards patience and precision, but punishes neglect or overcare. Avoiding these common mistakes will keep your plants thriving and your harvest profitable.

💧 1. Overwatering and Poor Drainage
Hemp roots love oxygen as much as they love water. Many beginners drown their plants by watering too frequently or using heavy, compacted soil that traps moisture. Overwatering leads to root rot, yellowing leaves, and stunted growth.
✅ Fix: Use well-draining loamy soil and let the top inch dry out before watering again. Install drip irrigation or fabric pots to improve airflow and root oxygenation.
🌱 2. Ignoring Soil pH and Nutrient Balance
Soil pH directly affects how hemp absorbs nutrients. When pH drifts out of range (ideal is 6.0–7.0), nutrients become locked out even if they’re present in the soil. Overfeeding synthetic fertilizers can also cause nutrient burn or toxic salt buildup.
✅ Fix: Test your soil and water pH weekly, use organic compost teas and microbial inoculants, and feed with a balanced NPK schedule that shifts appropriately between vegetative and flowering phases.
☀️ 3. Poor Light Exposure or Light Stress
Hemp is a light-hungry crop, and inadequate sunlight reduces both flower density and CBD potency. On the other hand, placing lights too close indoors can cause light burn and dry, bleached leaves.
✅ Fix: Provide 6–8 hours of direct sunlight outdoors or a consistent 18-hour light cycle indoors during the vegetative stage. Adjust light height regularly to maintain proper distance (12–24 inches depending on fixture type).
🧬 4. Using Uncertified or Poor Genetics
Not all hemp seeds are created equal. Low-quality or uncertified seeds often result in THC spikes, uneven growth, or poor CBD ratios — a costly risk for growers under strict hemp laws.
✅ Fix: Always source certified, feminized, high-CBD, low-THC hemp seeds from reputable breeders. Check for Certificates of Analysis (COAs) and ensure your strain is compliant with your local regulations.
🕷️ 5. Neglecting Pest and Disease Prevention
Waiting until you see pests to act is too late. Spider mites, aphids, and bud rot can devastate a crop within days. Many growers fail to apply consistent preventive pest control or proper airflow, allowing mold and mildew to thrive.
✅ Fix: Implement Integrated Pest Management (IPM) from day one — use neem oil, beneficial insects, and companion plants like marigold or basil. Keep humidity controlled and maintain clean grow spaces.
⏰ 6. Harvesting Too Early or Too Late
Harvest timing directly affects CBD and THC content. Harvesting early yields weak CBD levels, while waiting too long can increase THC beyond the legal limit. Both scenarios lead to lost profit or crop destruction.
✅ Fix: Use a magnifying glass to monitor trichomes — harvest when most turn milky white with 10–15% amber. Always test THC levels before cutting your crop.
🧪 7. Skipping Regular Testing and Record Keeping
Many growers overlook compliance and documentation — a critical part of legal hemp farming. Without lab testing and proper records, it’s difficult to prove that your hemp meets federal or regional standards.
✅ Fix: Keep a grower’s logbook documenting seed source, planting dates, nutrient schedules, and test results. Partner with certified labs to test THC and CBD concentrations before and after harvest.
⚖️ 8. Neglecting Post-Harvest Care
Even a perfect grow can fail at the finish line. Improper drying, curing, or storage can cause mold growth, loss of terpenes, or reduced CBD potency.
✅ Fix: Dry hemp slowly in a controlled environment (60–70°F, 50–60% humidity) and cure in glass jars for at least 2–4 weeks to lock in flavor, aroma, and potency.
🌾 Final Thoughts on Avoiding Hemp Growing Mistakes
Medicinal hemp rewards mindfulness. Every grower mistake — from watering habits to harvest timing — teaches something new. By mastering the balance between environment, nutrients, and compliance, you’ll avoid costly setbacks and cultivate consistent, high-quality CBD hemp that meets both wellness and regulatory standards.
Remember: Hemp doesn’t just grow in soil — it grows through experience. 🌱
🌿 Profit Potential and Future of the Medicinal Hemp Industry
Medicinal hemp isn’t just a plant — it’s a fast-growing global industry redefining agriculture, wellness, and sustainability. The increasing consumer demand for CBD-rich hemp products has made hemp farming one of the most profitable agricultural opportunities of the decade. For growers who master compliance, quality, and organic practices, the potential rewards are both financial and environmental.

💰 Understanding Hemp’s Profit Margins
The profitability of hemp cultivation depends on several factors — yield per acre, CBD concentration, growing method, and market prices. On average:
- Outdoor hemp farms can yield 1,500–2,500 pounds of dry biomass per acre.
- High-quality CBD-rich flower may sell for $200–$500 per pound (depending on region and purity).
- CBD extraction can produce up to 50–75 pounds of oil per acre, translating to significant returns.
Smaller boutique farms often focus on hand-trimmed, organic CBD flowers, fetching premium prices from wellness brands and dispensaries. Meanwhile, large-scale operations prioritize biomass for CBD oil extraction to serve bulk markets and manufacturers.
💡 Pro Tip: Diversify your product streams — sell dried flower, biomass, and even hemp seed oil or fiber for added income stability.
🌎 Global Growth and Market Trends
According to market analysts, the global hemp-derived CBD market is projected to exceed $25 billion by 2030 as consumer awareness and legalization expand across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific.
Major factors driving this growth include:
- Increased acceptance of natural, plant-based remedies for anxiety, pain, and sleep.
- Rising demand for organic and sustainably grown hemp.
- Innovation in CBD-infused wellness products — from supplements and skincare to beverages and pet health.
Countries like the U.S., Canada, and Switzerland lead the charge, while emerging markets in Thailand, Australia, and South Africa are rapidly adopting hemp legislation to attract investment and job creation.
🌾 Sustainability and Regenerative Farming Opportunities
Beyond profit, hemp is hailed as a sustainability champion. Its deep roots improve soil health, absorb carbon, and require minimal pesticides — making it ideal for regenerative agriculture.
Forward-thinking hemp farmers are integrating crop rotation, living soil, and zero-waste processing to reduce their environmental footprint while maintaining premium quality. These eco-friendly practices not only appeal to conscious consumers but also help farms qualify for organic certifications that raise market value.
🌱 Sustainability Tip: Reuse spent hemp biomass for composting, biochar, or hempcrete — turning waste into long-term value.
🚀 The Future of Medicinal Hemp Farming
As global regulations evolve, hemp cultivation for medicinal and wellness purposes will continue to expand into mainstream agriculture. Expect to see:
- Advances in genetics — producing ultra-high CBD and novel cannabinoids like CBG and CBN.
- AI-driven farming technology to monitor crop health and optimize harvests.
- Blockchain traceability for transparent supply chains and verified purity.
- Integration with pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries, pushing hemp beyond the wellness niche.
The hemp industry is no longer experimental — it’s foundational. With rising public demand and supportive legislation, the future belongs to growers who combine compliance, innovation, and sustainability.
🌿 Final Thoughts on Profit and Progress
Medicinal hemp represents more than income — it’s a movement toward natural health, rural revival, and green entrepreneurship. Whether you’re a small homestead grower or a large-scale cultivator, the opportunity is real and growing.
By staying compliant, investing in genetics, and nurturing your soil responsibly, you can cultivate both CBD-rich harvests and a sustainable legacy in this booming green economy.
🌿 Conclusion: Cultivating Wellness, Profit, and Sustainability Through Medicinal Hemp
Growing medicinal hemp is more than just agriculture — it’s a journey that unites science, nature, and purpose. From seed to harvest, every stage reflects your dedication to producing CBD-rich, compliant, and environmentally responsible hemp. With the right genetics, soil care, and legal awareness, you’re not simply growing plants — you’re cultivating wellness and opportunity.
As global demand for hemp-derived CBD products continues to rise, today’s growers hold the power to shape the future of sustainable, plant-based medicine. By focusing on organic practices, regenerative soil systems, and precision harvesting, small and large farmers alike can build thriving businesses rooted in integrity and quality.
Remember: hemp rewards patience and consistency. The more you learn its rhythm — from germination and nutrient cycles to harvest timing and post-processing — the better your yields, your compliance, and your peace of mind.
Medicinal hemp truly embodies the spirit of modern farming: sustainable, profitable, and healing. As legalization expands and public awareness grows, the world is embracing this plant not as a trend, but as a transformation — one that connects growers, patients, and nature in a shared pursuit of wellness. 🌱
At the end of your article, add a short linking paragraph to reinforce topical authority and reader navigation:
💬 If you enjoyed this guide, explore more growing tutorials on our site — from Growing Feminized Seeds Indoors and How to Grow Weed in an AeroGarden to Top 10 Living Soil Brands. Each article is designed to help you grow healthier, more potent, and sustainable cannabis plants, whether indoors or outdoors.
References and Sources:
- The Agriculture Improvement Act of 2018 (commonly called the 2018 Farm Bill) removed hemp (defined as “cannabis sativa, … with a delta-9 THC concentration of not more than 0.3 percent on a dry weight basis”) from the Controlled Substances Act. Congress.gov, U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Food and Drug Law Institute (FDLI), Congress.gov.
- The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) runs the domestic hemp production program; growers must be licensed under a state, tribal or USDA plan. ams.usda.gov, Kansas department of Agriculture.
- In the European Union, hemp cultivation requires that the THC content of the variety must not exceed 0.3% and must use certified seed varieties listed in the EU catalogue. Agriculture and Rural Development.






